- 电池电源模块设置
- 概述
- 基本电池设置(默认) {#basic_settings}
- 电池芯数(串联)
- Full Voltage (per cell)
- 空电电压(每个电芯)
- 分压器
- 安培/伏特 {#current_divider}
- 基于电压估计的负载补偿 {#load_compensation}
- 基于电流的负载补偿(推荐) {#current_based_load_compensation}
- Thrust-based Load Compensation {#thrust_based_load_compensation}
- Voltage-based Estimation Fused with Current Integration {#current_integration}
电池电源模块设置
该主题解释了如何进行电源设置
注只有兼容的硬件才能使用PX4的电池监控功能。 在大多数情况下,这意味着测量电池电压的电源模块,并且还可以测量电池和飞机之间的电流。
概述
电源设置的目标是提供对剩余电池百分比(和容量)的良好估计,以便飞机不会电力耗尽和坠毁(或电池因深度放电而损坏)。
PX4提供了许多(逐步更有效)的方法,可用于估计容量:
- 基本电池设置(默认值):将原始测量电压与“空”和“满”电压之间的范围进行比较。 这样的估计较为粗略,因为测量的电压(及其相应的容量)将在负载下产生波动。
- 基于电压的负载补偿估计:抵消负载对电池容量计算的影响。
- 基于电流积分的电压估计:通过基于电流的已消耗电荷估计,对基于负载补偿电压的估计出的可用容量进行补充。 这样的容量估计相当于智能电池的容量估计。
后来的方法建立在前面的方法上。 您使用的方法取决于飞机的电源模块是否可以测量电流。
基本电池设置(默认) {#basic_settings}
注当测量电压在负载下变化时,由于估计电压的波动,该默认/基本功率配置会导致相对粗略的估计。
基本电池设置将PX4配置为使用默认方法进行容量估算。 该方法将测量的原始电池电压与“空”和“满”状态电池电压之间的范围进行比较(按电池数量换算)。
要配置基本设置, 请执行以下操作:
- 打开 QGroundControl 并连接上飞机。
- 在上面的工具条中选择 齿轮 按钮,然后在左面的工具条中选择 电源 按钮。
您将看到表征电池的基本设置。 以下部分说明了为每个字段设置的值。
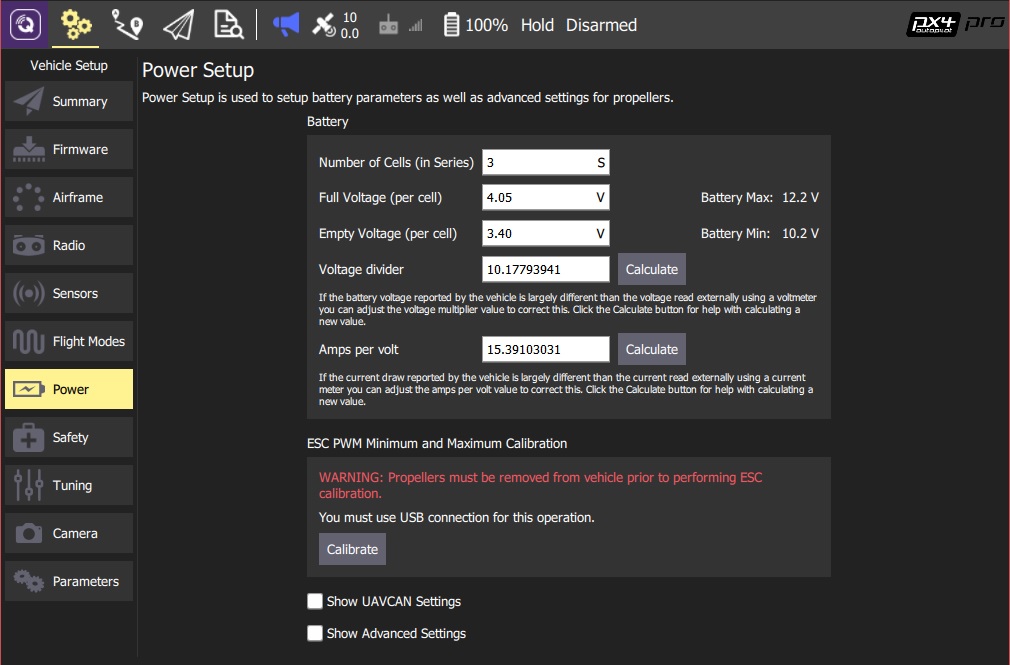
注以下基本设置对应于参数:BAT_N_CELLS,BAT_V_EMPTY,BAT_V_CHARGED。
电池芯数(串联)
这设置了电池中串联的电池数量。 通常,这将作为数字写在电池上,后跟“S”(例如“3S”,“5s”)。
注单个原电池单元的电压取决于电池类型的化学特性。 最常见的无人机电池类型(锂聚合物 - LiPo)的标称电池电压为3.7V。 为了实现更高的电压(其将更有效地为飞机提供动力),多个电池以*串联</ 0>连接。 然后,端子处的电池电压是单个电芯电压的倍数。
如果未提供电池数量,您可以通过将电池电压除以单个电池的标称电压来计算它。 下表显示了LiPo电池的电压 - 电池关系:
- 1S - 3.7V
- 2S - 7.4V
- 3S - 11.1V
- 4S - 14.8V
- 5S - 18.5V
- 6S - 22.2V
Full Voltage (per cell)
这设置每个电池单元的*标称</ 0>最大电压(电池单元状态是“满”的最低电压)。
该值应设置为略低于电池的标称最大电压(LiPo为4.2V),但不能太低,以至于飞行几分钟后估计的容量仍为100%。 默认值通常适用于LiPo电池。
注充电后,满电池的电压可能会随着时间的推移而下降一小部分。 设置略低于最大值可以补偿此下降。
空电电压(每个电芯)
这设置了每个电池的标称最小安全电压(低于此电压使用可能会损坏电池)。
注没有单个值表示电池是空的。 如果选择的值太低,电池可能会因深度放电而损坏(和/或飞机可能会坠毁)。 如果您选择的值太高,可能会不必要地限制您的飞行。
LiPo电池的经验法则:
- 无负载3.7V是保守的最小值。
- 负载下3.5 V(飞行时)接近真实最小值。 在这个电压下, 你应该立即降落。
- 负载下3.2V将对电池造成损坏。
提示低于保守范围,越早给电池充电越好 - 它会持续更长时间并且更慢地减少容量。
分压器
如果您通过电源模块或飞行控制器的模数转换器测量飞行器的电压,您应该每次检查并校准测量模块。 为了校准您需要一个万用表。
校准分压器最简单的方法是使用QGroundControl 按照 Setup > Power Setup 一步步完成校准(QGroundControl User Guide)。
Note 此设置对应于参数 BAT_A_PER_V。
安培/伏特 {#current_divider}
Tip 如果您使用基本配置,此设置不需要(没有负载补偿等)。
如果您使用 Current-based Load Compensation 或 Current Integration 安培/伏特分压器必须校准。
校准分压器最简单的方法是使用QGroundControl 按照 Setup > Power Setup 一步步完成校准(QGroundControl User Guide)。
基于电压估计的负载补偿 {#load_compensation}
Note 负载参数配置良好时,电池容量估计的电压更加稳定,在上升和下降过程中变化较小。
负载补偿尝试抵消,使用 basic configuration 时,负载中测量电压/估计容量的波动。 通过估计 卸载 电压,使用这一电压(而不是测量电压)估计剩余电量。
Note 使用负载补偿,您仍然需要配置 basic configuration 。 空载电压 (BAT_V_EMPTY) 应该设置更高(高于没有补偿时)因为补偿电压被用来估计(通常低于空载时预期的休眠电池电压)。
PX4支持两种负载补偿方法,这些方法是由 setting 下面两个参数启用:
- BAT_R_INTERNAL - Current-based Load Compensation (推荐)。
- BAT_V_LOAD_DROP - Thrust-based Load Compensation。
基于电流的负载补偿(推荐) {#current_based_load_compensation}
这种负载补偿方式基于电流测量来确定负载。 It is far more accurate than Thrust-based Load Compensation but requires that you have a current sensor.
To enable this feature:
- Set the parameter BAT_R_INTERNAL to to the internal resistance of your battery. > Tip There are LiPo chargers out there which can measure the internal resistance of your battery. A typical value is 5mΩ per cell but this can vary with discharge current rating, age and health of the cells.
- You should also calibrate the Amps per volt divider in the basic settings screen.
Thrust-based Load Compensation {#thrust_based_load_compensation}
This load compensation method estimates the load based on the total thrust that gets commanded to the motors.
Caution This method is not particularly accurate because there’s a delay between thrust command and current, and because the thrust in not linearly proportional to the current. Use Current-based Load Compensation instead if your vehicle has a current sensor.
To enable this feature:
- Set the parameter BAT_V_LOAD_DROP to how much voltage drop a cell shows under the load of full throttle.
Voltage-based Estimation Fused with Current Integration {#current_integration}
Note This is the most accurate way to measure relative battery consumption. If set up correctly with a healthy and fresh charged battery on every boot, then the estimation quality will be comparable to that from a smart battery (and theoretically allow for accurate remaining flight time estimation).
This method evaluates the remaining battery capacity by fusing the voltage-based estimate for the available capacity with a current-based estimate of the charge that has been consumed. It requires hardware that can accurately measure current.
To enable this feature:
First set up accurate voltage estimation using current-based load compensation.
Tip Including calibrating the Amps per volt divider setting.
Set the parameter BAT_CAPACITY to around 90% of the advertised battery capacity (usually printed on the battery label).
Note Do not set this value too high as this may result in a poor estimation or sudden drops in estimated capacity.
Additional information
The estimate of the charge that has been consumed over time is produced by mathematically integrating the measured current (this approach provides very accurate energy consumption estimates).
At system startup PX4 first uses a voltage-based estimate to determine the initial battery charge. This estimate is then fused with the value from current integration to provide a combined better estimate. The relative value placed on each estimate in the fused result depends on the battery state. The emptier the battery gets, the more of the voltage based estimate gets fused in. This prevents deep discharge (e.g. because it was configured with the wrong capacity or the start value was wrong).
If you always start with a healthy full battery, this approach is similar to that used by a smart battery.
Note Current integration cannot be used on its own (without voltage-based estimation) because it has no way to determine the initial capacity. Voltage-estimation allows you to estimate the initial capacity and provides ongoing feedback of possible errors (e.g. if the battery is faulty, or if there is a mismatch between capacity calculated using different methods).
