- TensorFlow.js 模型训练 *
TensorFlow.js 模型训练 *
与 TensorFlow Serving 和 TensorFlow Lite 不同,TensorFlow.js 不仅支持模型的部署和推断,还支持直接在 TensorFlow.js 中进行模型训练、
在 TensorFlow 基础章节中,我们已经用 Python 实现过,针对某城市在2013年-2017年的房价的任务,通过对该数据进行线性回归,即使用线性模型 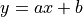 来拟合上述数据,此处
来拟合上述数据,此处  和
和 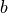 是待求的参数。
是待求的参数。
下面我们改用 TensorFlow.js 来实现一个 JavaScript 版本。
首先,我们定义数据,进行基本的归一化操作。
- import * as tf from '@tensorflow/tfjs'
- const xsRaw = tf.tensor([2013, 2014, 2015, 2016, 2017])
- const ysRaw = tf.tensor([12000, 14000, 15000, 16500, 17500])
- // 归一化
- const xs = xsRaw.sub(xsRaw.min())
- .div(xsRaw.max().sub(xsRaw.min()))
- const ys = ysRaw.sub(ysRaw.min())
- .div(ysRaw.max().sub(ysRaw.min()))
接下来,我们来求线性模型中两个参数 a 和 b 的值。
使用 loss() 计算损失;使用 optimizer.minimize() 自动更新模型参数。
- const a = tf.scalar(Math.random()).variable()
- const b = tf.scalar(Math.random()).variable()
- // y = a * x + b.
- const f = (x: tf.Tensor) => a.mul(x).add(b)
- const loss = (pred: tf.Tensor, label: tf.Tensor) => pred.sub(label).square().mean() as tf.Scalar
- const learningRate = 1e-3
- const optimizer = tf.train.sgd(learningRate)
- // 训练模型
- for (let i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
- optimizer.minimize(() => loss(f(xs), ys))
- }
- // 预测
- console.log(`a: ${a.dataSync()}, b: ${b.dataSync()}`)
- const preds = f(xs).dataSync() as Float32Array
- const trues = ys.arraySync() as number[]
- preds.forEach((pred, i) => {
- console.log(`x: ${i}, pred: ${pred.toFixed(2)}, true: ${trues[i].toFixed(2)}`)
- })
从下面的输出样例中我们可以看到,已经拟合的比较接近了。
- a: 0.9339302778244019, b: 0.08108722418546677
- x: 0, pred: 0.08, true: 0.00
- x: 1, pred: 0.31, true: 0.36
- x: 2, pred: 0.55, true: 0.55
- x: 3, pred: 0.78, true: 0.82
- x: 4, pred: 1.02, true: 1.00
可以直接在浏览器中运行,完整的 HTML 代码如下:
- <html>
- <head>
- <script src="http://unpkg.com/@tensorflow/tfjs/dist/tf.min.js"></script>
- <script>
- const xsRaw = tf.tensor([2013, 2014, 2015, 2016, 2017])
- const ysRaw = tf.tensor([12000, 14000, 15000, 16500, 17500])
- // 归一化
- const xs = xsRaw.sub(xsRaw.min())
- .div(xsRaw.max().sub(xsRaw.min()))
- const ys = ysRaw.sub(ysRaw.min())
- .div(ysRaw.max().sub(ysRaw.min()))
- const a = tf.scalar(Math.random()).variable()
- const b = tf.scalar(Math.random()).variable()
- // y = a * x + b.
- const f = (x) => a.mul(x).add(b)
- const loss = (pred, label) => pred.sub(label).square().mean()
- const learningRate = 1e-3
- const optimizer = tf.train.sgd(learningRate)
- // 训练模型
- for (let i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
- optimizer.minimize(() => loss(f(xs), ys))
- }
- // 预测
- console.log(`a: ${a.dataSync()}, b: ${b.dataSync()}`)
- const preds = f(xs).dataSync()
- const trues = ys.arraySync()
- preds.forEach((pred, i) => {
- console.log(`x: ${i}, pred: ${pred.toFixed(2)}, true: ${trues[i].toFixed(2)}`)
- })
- </script>
- </head>
- </html>
