- 语句和表达式
- 声明语句
- 表达式语句
- 以上表达式语句中的部分例子引用自 Rust Reference
- 以上表达式语句中的部分例子引用自 Rust Reference
语句和表达式
rust是一个基于表达式的语言,不过它也有语句。rust只有两种语句:声明语句和表达式语句,其他的都是表达式。基于表达式是函数式语言的一个重要特征,表达式总是返回值。
声明语句
rust的声明语句可以分为两种,一种为变量声明语句,另一种为Item声明语句。
变量声明语句。主要是指
let语句,如:let a = 8;let b: Vec<f64> = Vec::new();let (a, c) = ("hi", false);
由于let是语句,所以不能将let语句赋给其他值。如下形式是错误的:
let b = (let a = 8);
rustc编译器会给出错误信息:
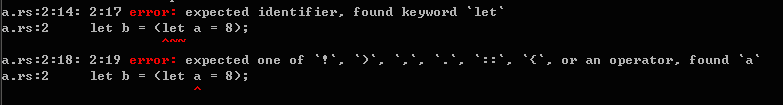
Item声明。是指函数(function)、结构体(structure)、类型别名(type)、静态变量(static)、特质(trait)、实现(implementation)或模块(module)的声明。这些声明可以嵌套在任意块(block)中。关于Item声明,Rust Reference中的描述如下:
An item declaration statement has a syntactic form identical to an item declaration within a module. Declaring an item — a function, enumeration, structure, type, static, trait, implementation or module — locally within a statement block is simply a way of restricting its scope to a narrow region containing all of its uses; it is otherwise identical in meaning to declaring the item outside the statement block.
当然,这里不能展开讲这些Item都是如何声明的,详情请看RustPrimer的其他相关章节。
表达式语句
表达式语句,由一个表达式和一个分号组成,即在表达式后面加一个分号就将一个表达式转变为了一个语句。所以,有多少种表达式,就有多少种表达式语句。
rust有许多种表达式:
字面表达式(literal expression)
(); // unit type"hello"; // string type'1'; // character type15; // integer type
元组表达式(Tuple expression):
(0.0, 4.5);("a", 4usize, true);
通常不使用一个元素的元组,不过如果你坚持的话,rust也是允许的,不过需要在元素后加一个逗号:
(0,); // single-element tuple(0); // zero in parentheses
结构体表达式(structure expression)
由于结构体有多种形式,所以结构体表达式也有多种形式。Point {x: 10.0, y: 20.0};TuplePoint(10.0, 20.0);let u = game::User {name: "Joe", age: 35, score: 100_000};some_fn::<Cookie>(Cookie);
结构体表达式一般用于构造一个结构体对象,它除了以上从零构建的形式外,还可以在另一个对象的基础上进行构建:
let base = Point3d {x: 1, y: 2, z: 3};Point3d {y: 0, z: 10, .. base};
块表达式(block expression):
块表达式就是用花括号{}括起来的一组表达式的集合,表达式间一般以分号分隔。块表达式的值,就是最后一个表达式的值。let x: i32 = { println!("Hello."); 5 };
如果以语句结尾,则块表达式的值为
():let x: () = { println!("Hello."); };
范围表达式(range expression):
可以使用范围操作符..来构建范围对象(variant ofstd:): :Range
:Range1..2; // std: :Range
:Range3..; // std: :RangeFrom
:RangeFrom..4; // std: :RangeTo
:RangeTo..; // std: :RangeFull
:RangeFull
if表达式(if expression):
let a = 9;let b = if a%2 == 0 {"even"} else {"odd"};
除了以上这些外,还有许多,如:
- path expression
- mehond-call expression
- field expression
- array expression
- index expression
- unary operator expression
- binary operator expression
- return expression
- grouped expression
- match expression
- if expression
- lambda expression
- … …
这里无法详细展开,读者可以到Rust Reference去查看。
以上表达式语句中的部分例子引用自Rust Reference
