- Virtual DOM
- 总结
- 总结
Virtual DOM
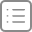
Virtual DOM 这个概念相信大部分人都不会陌生,它产生的前提是浏览器中的 DOM 是很“昂贵"的,为了更直观的感受,我们可以简单的把一个简单的 div 元素的属性都打印出来,如图所示:
可以看到,真正的 DOM 元素是非常庞大的,因为浏览器的标准就把 DOM 设计的非常复杂。当我们频繁的去做 DOM 更新,会产生一定的性能问题。
而 Virtual DOM 就是用一个原生的 JS 对象去描述一个 DOM 节点,所以它比创建一个 DOM 的代价要小很多。在 Vue.js 中,Virtual DOM 是用 VNode 这么一个 Class 去描述,它是定义在 src/core/vdom/vnode.js 中的。
export default class VNode {tag: string | void;data: VNodeData | void;children: ?Array<VNode>;text: string | void;elm: Node | void;ns: string | void;context: Component | void; // rendered in this component's scopekey: string | number | void;componentOptions: VNodeComponentOptions | void;componentInstance: Component | void; // component instanceparent: VNode | void; // component placeholder node// strictly internalraw: boolean; // contains raw HTML? (server only)isStatic: boolean; // hoisted static nodeisRootInsert: boolean; // necessary for enter transition checkisComment: boolean; // empty comment placeholder?isCloned: boolean; // is a cloned node?isOnce: boolean; // is a v-once node?asyncFactory: Function | void; // async component factory functionasyncMeta: Object | void;isAsyncPlaceholder: boolean;ssrContext: Object | void;fnContext: Component | void; // real context vm for functional nodesfnOptions: ?ComponentOptions; // for SSR cachingfnScopeId: ?string; // functional scope id supportconstructor (tag?: string,data?: VNodeData,children?: ?Array<VNode>,text?: string,elm?: Node,context?: Component,componentOptions?: VNodeComponentOptions,asyncFactory?: Function) {this.tag = tagthis.data = datathis.children = childrenthis.text = textthis.elm = elmthis.ns = undefinedthis.context = contextthis.fnContext = undefinedthis.fnOptions = undefinedthis.fnScopeId = undefinedthis.key = data && data.keythis.componentOptions = componentOptionsthis.componentInstance = undefinedthis.parent = undefinedthis.raw = falsethis.isStatic = falsethis.isRootInsert = truethis.isComment = falsethis.isCloned = falsethis.isOnce = falsethis.asyncFactory = asyncFactorythis.asyncMeta = undefinedthis.isAsyncPlaceholder = false}// DEPRECATED: alias for componentInstance for backwards compat./* istanbul ignore next */get child (): Component | void {return this.componentInstance}}
可以看到 Vue.js 中的 Virtual DOM 的定义还是略微复杂一些的,因为它这里包含了很多 Vue.js 的特性。这里千万不要被这些茫茫多的属性吓到,实际上 Vue.js 中 Virtual DOM 是借鉴了一个开源库 snabbdom 的实现,然后加入了一些 Vue.js 特色的东西。我建议大家如果想深入了解 Vue.js 的 Virtual DOM 前不妨先阅读这个库的源码,因为它更加简单和纯粹。
总结
其实 VNode 是对真实 DOM 的一种抽象描述,它的核心定义无非就几个关键属性,标签名、数据、子节点、键值等,其它属性都是都是用来扩展 VNode 的灵活性以及实现一些特殊 feature 的。由于 VNode 只是用来映射到真实 DOM 的渲染,不需要包含操作 DOM 的方法,因此它是非常轻量和简单的。
Virtual DOM 除了它的数据结构的定义,映射到真实的 DOM 实际上要经历 VNode 的 create、diff、patch 等过程。那么在 Vue.js 中,VNode 的 create 是通过之前提到的 createElement 方法创建的,我们接下来分析这部分的实现。
原文: https://ustbhuangyi.github.io/vue-analysis/data-driven/virtual-dom.html